Students observe teacherled demonstrations, and build and evaluate simple models to understand the greenhouse effect, the role of increased greenhouse gas concentration in global warming, and the implications of global warming for engineers, themselves and the Earth In an associated literacy activOff the surface is absorbed and reradiated into the atmosphere, where much of it is absorbed by the greenhouse gases This is known as the greenhouse effect BACKGROUND Use the following terms to label the diagram belowThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, but the extra gases produced by human activity are making it stronger We are now adding to these gases faster than oceans and plants can absorb them — the greenhouse effect is being 'enhanced' by humans There is strong evidence that recent changes are unprecedented and not due to natural
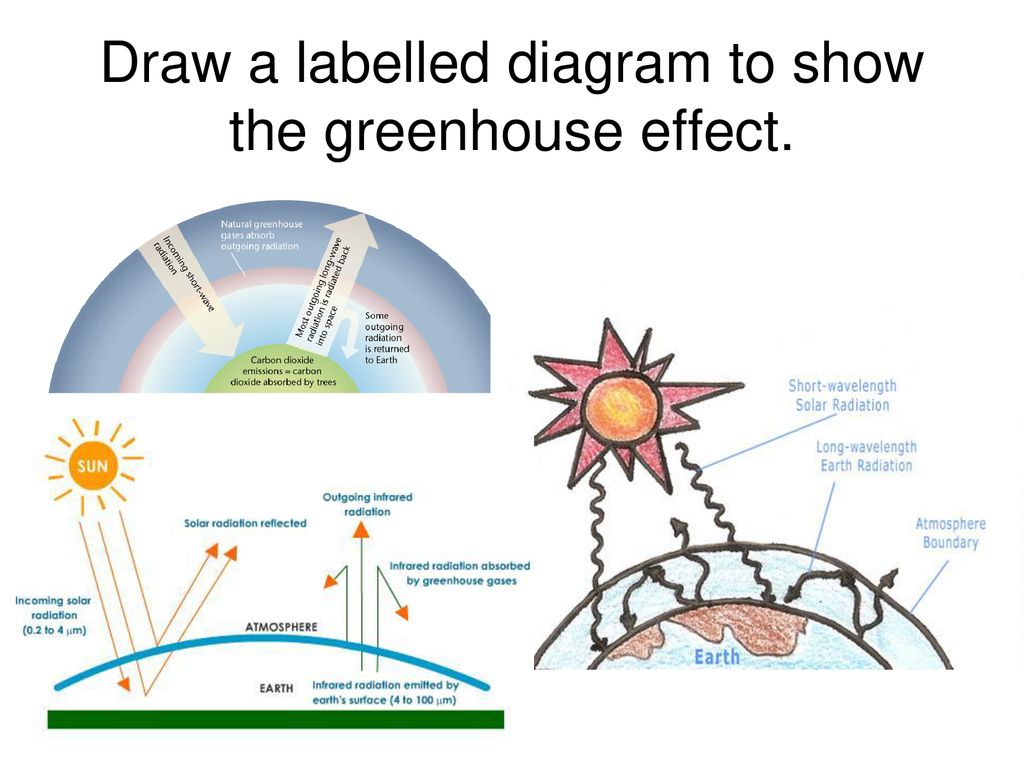
Lesson Ppt Download
Greenhouse effect diagram labeled
Greenhouse effect diagram labeled-Greenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees Celsius ,002 greenhouse effect stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect stock video clips of 1 greenhouse effect diagram commercial spraying water on plants greenhouse gas effect global warming posters sun earth diagram energy poster global warming global warming solutions sun radiating to a plant




Stoichiometry Of Gases Chem 1305 Introductory Chemistry
Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect" 1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat from escaping Longlived gases that remain semipermanently in the atmosphere and do not respondSurrounding the greenhouse effect and global warming Here's how you can help Task 1 Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect Label it carefully Task 2 Below your diagram write a concise paragraph that explains the diagram Write neatly and use correct English! The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, theActivity 11 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 7 – 9 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will do a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect, and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 The Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinionGlobal Warming The Greenhouse Effect Model Storyboard That is a great way for students to combine images and text in a creative way to produce quick and clear scientific diagrams Students are going to recreate a model of the greenhouse effect using arrows to show how radiation moves
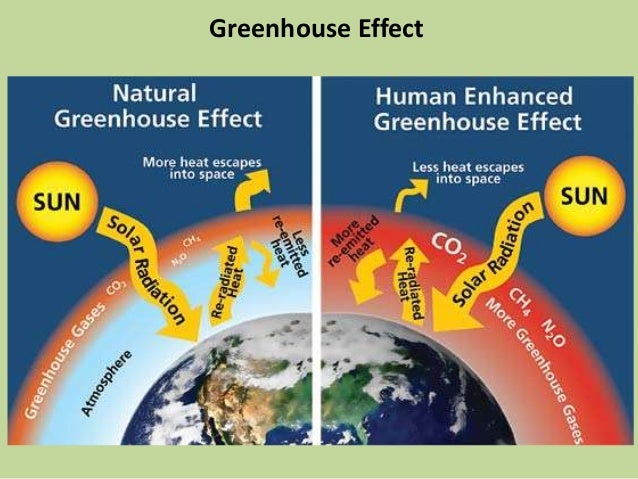
Observe the Greenhouse Effect in a Jar This experiment gets kids exploring how a greenhouse works, and in turn how greenhouse gases affect the Earth's atmosphere Your child will strengthen observation and recording skills, work with a control, and draw conclusions And bonus this is a great outdoor activity! An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThink about it Draw a picture or diagram that shows the relationship between carbon dioxide, the carbon cycle, and the greenhouse effect Be sure to label and explain your drawing/diagram Figure 2 The Natural and Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Source EPA
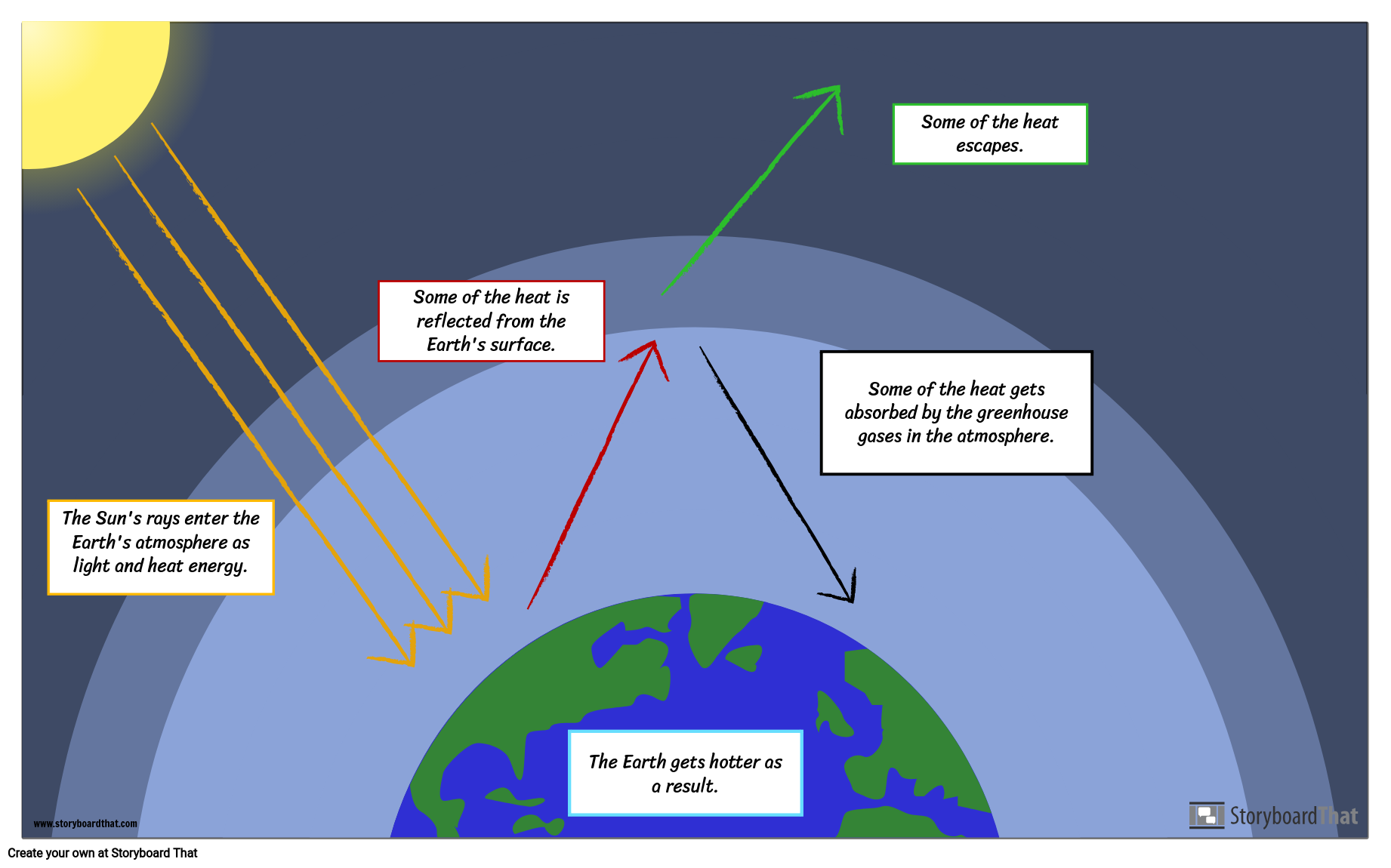



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram
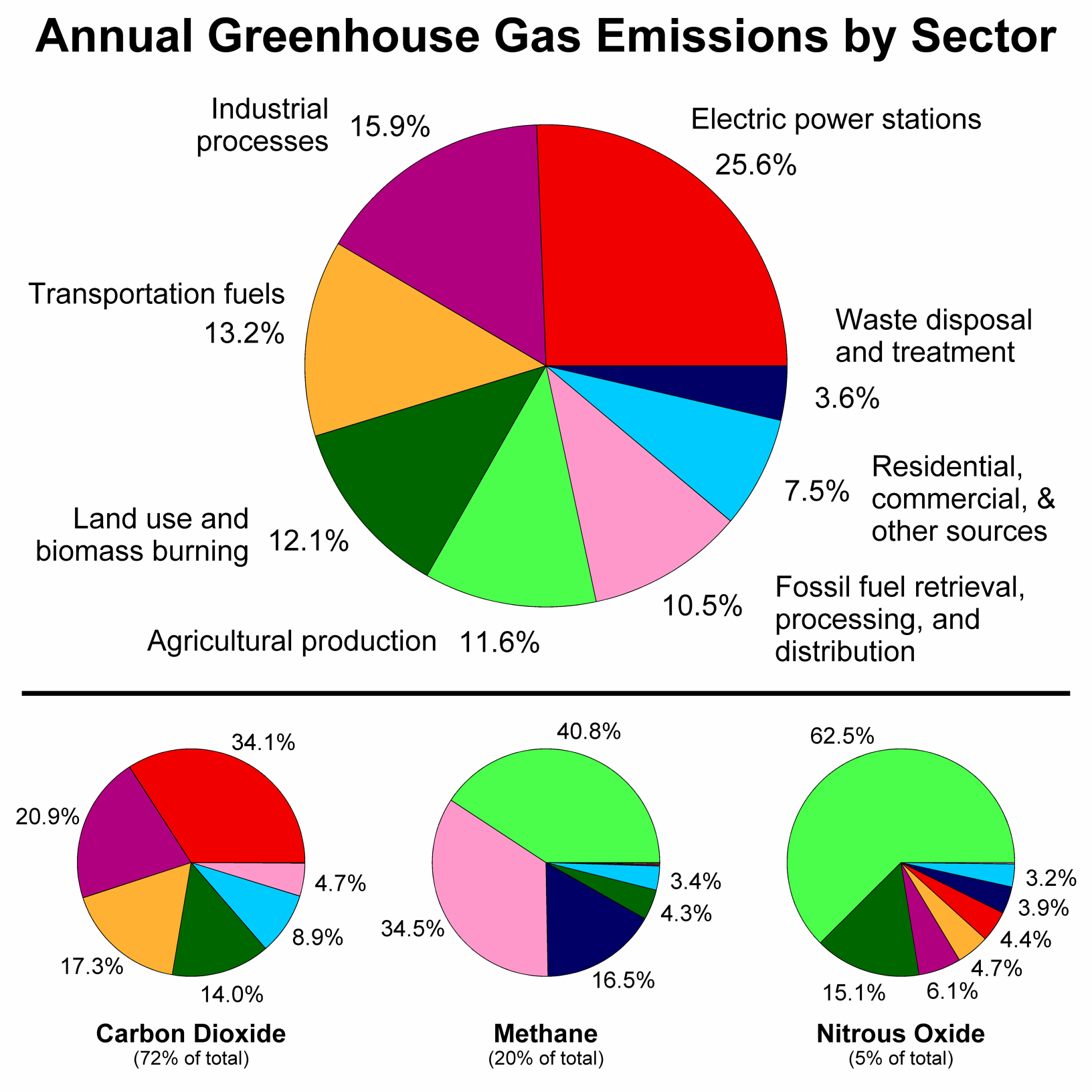



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons
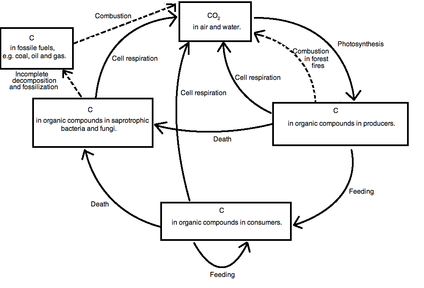
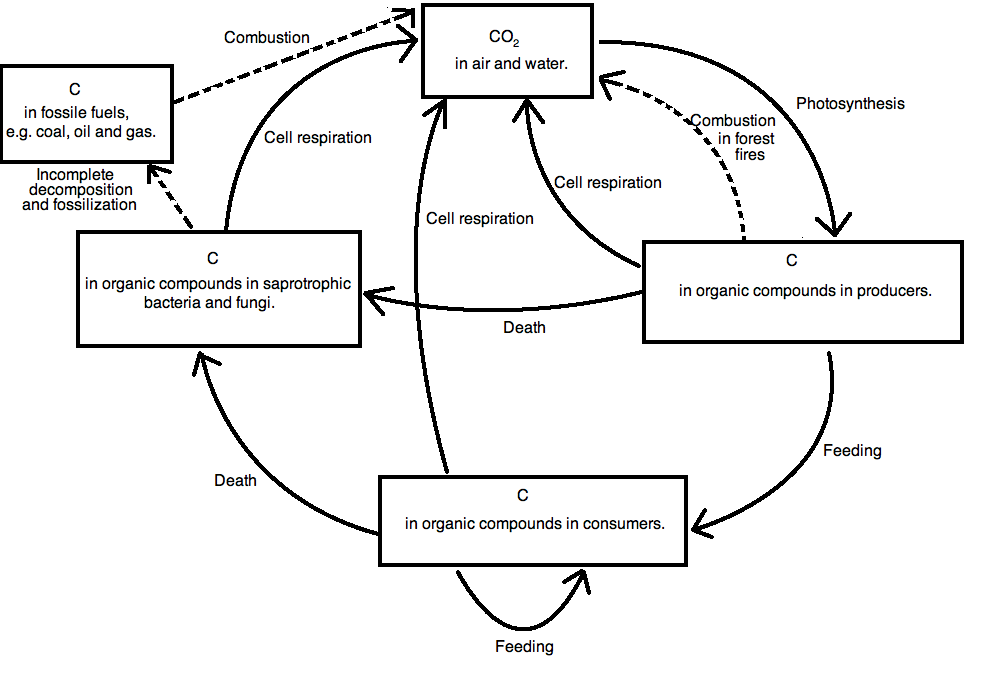
Draw a diagram and label to EXPLAIN the greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a process that warms the atmosphere due to the absorption of radiation from the greenhouse gases Explain how the Carbon Cycle is involved in global climate changeThe greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would beIT adds to the greenhouse effect Draw a diagram and label to EXPLAIN the greenhouse effect Explain how the Carbon Cycle is involved in global climate change Carbon is continuously exchanged and recycled among the reservoirs through natural processes As plants photosynthesize during the growing season, they remove large amounts of CO2 from



2



1
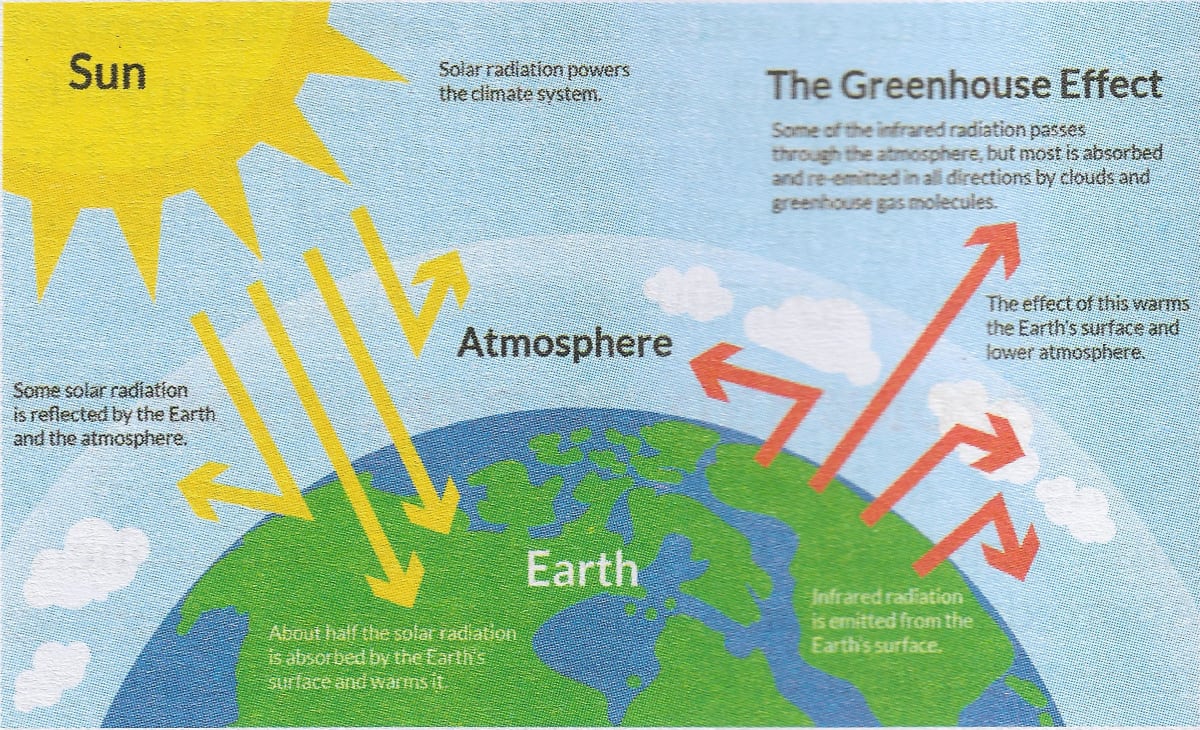
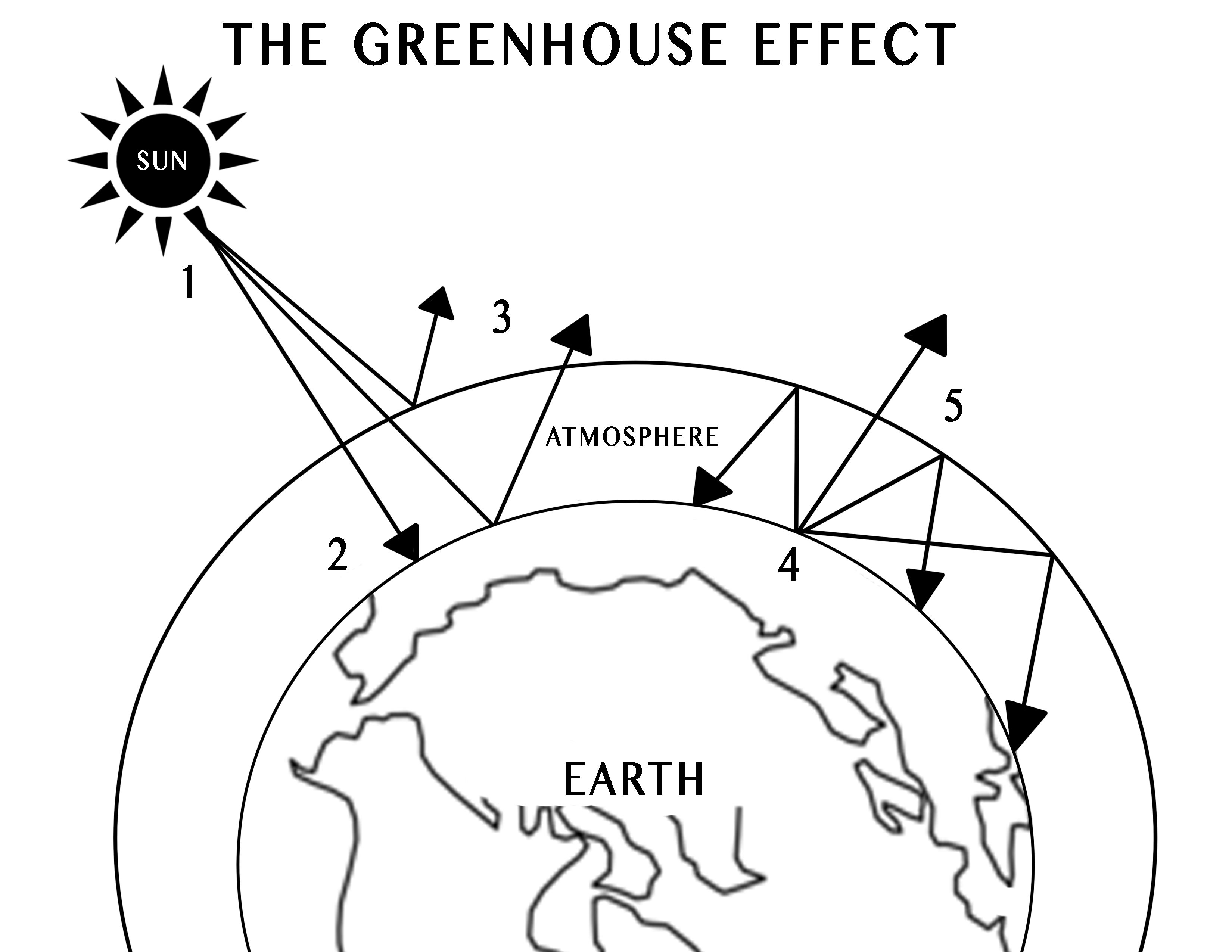
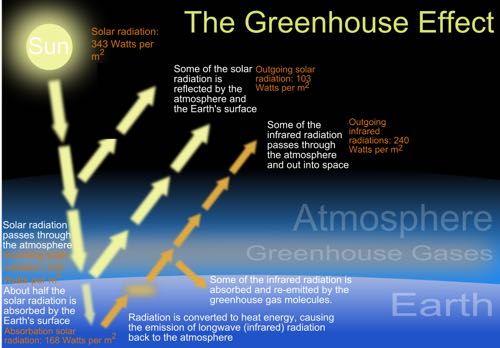
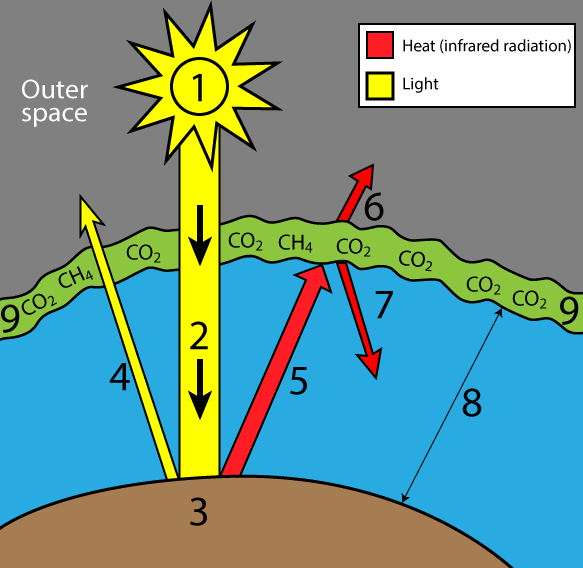
English This diagram shows how the greenhouse effect works Incoming solar radiation to the Earth equals 341 watts per square meter (Trenberth et al, 09) Some of the solar radiation is reflected back from the Earth by clouds, the atmosphere, and the Earth's surface (102 watts per square meter) Some of the solar radiation passes through the atmosphereHow the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphereThis alters the radiative balance of the earth (see Figure A1) and results in a warming of the earth's surface The major greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrogenated chlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), tropospheric ozone (O 3 ), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O)
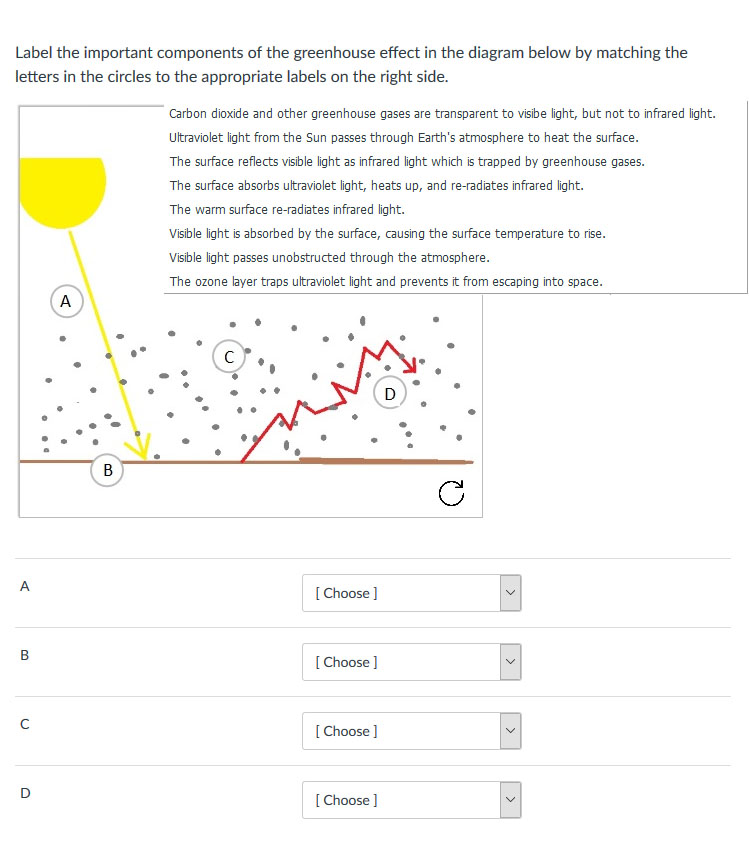



Solved Label The Important Components Of The Greenhouse Chegg Com



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Activity 12 Understanding the Greenhouse Effect Grades 5 – 6 Description In Part 1 Modeling the Greenhouse Effect, students will complete a lab that demonstrates the greenhouse effect and will discuss the results of the lab In Part 2 Earth's Energy Balance, students will color in a diagram, answer opinion questions, and perform a skitThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect"Use the back of this worksheet if necessary




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng
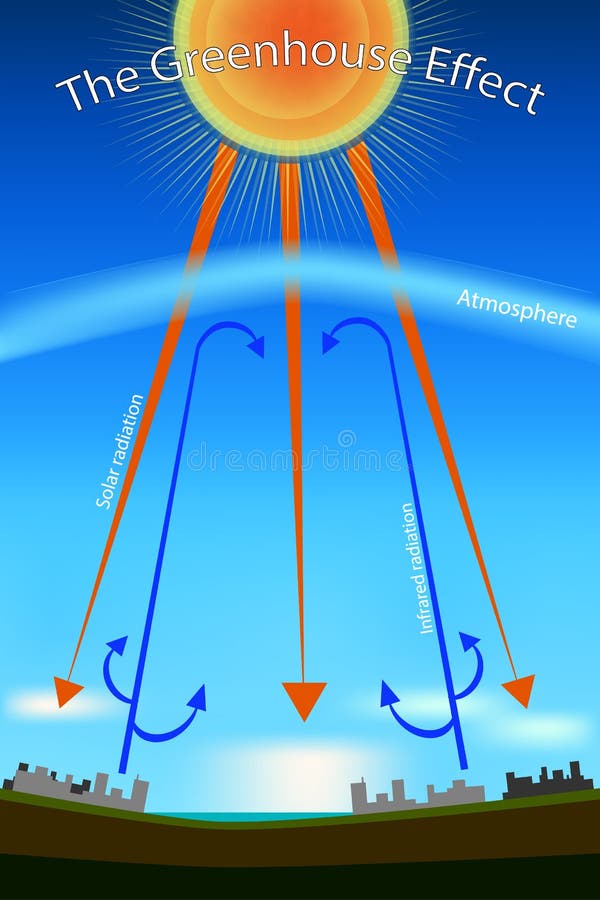
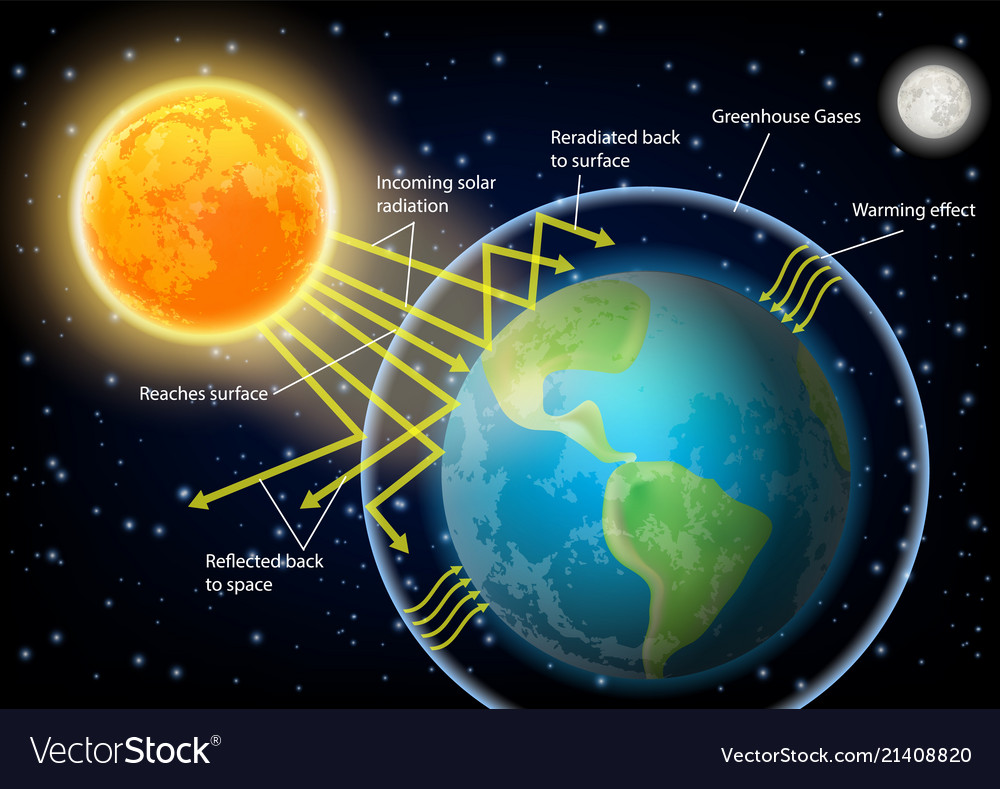
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trapGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearThe diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Works Global Warming Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Lesson Ppt Download
The Greenhouse Effect The picture below shows the greenhouse effect Light from the sun passes through the atmosphere and is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it Greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, act like a blanket, trapping heat near the surface and raising the temperature It is a natural process that warms the planetResults in a greenhouse effect, which refers to the absorption of longwave radiation by gases in the atmosphere The greenhouse effect results in Earth's temperature being warm enough to sustain life The concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere determine the average global temperature Source The Saskatchewan Environmental SocietyUse this greenhouse effect diagram to help students understand how humans can impact the world around them This science worksheet (that is also a coloring page) outlines how the greenhouse effect can really heat up the planet's surface Catered to fourth graders, this worksheet touches on several topics related to Earth & space science
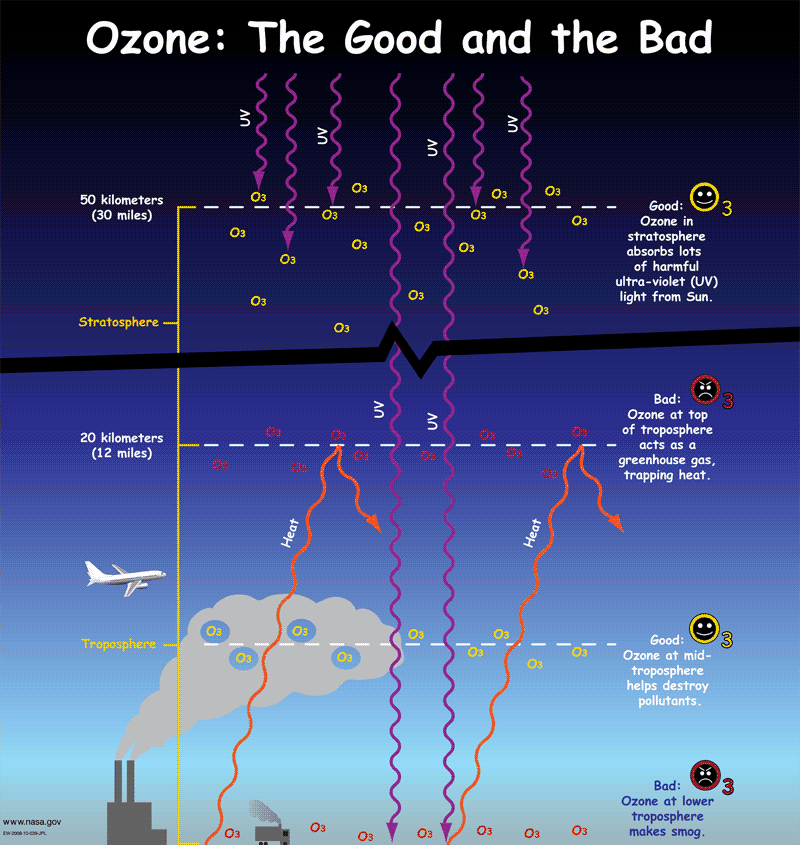



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Stoichiometry Of Gases Chem 1305 Introductory Chemistry
Without premise 3, you can still pretty convincingly describe the Coriolis Effect on objects moving due north or due south The Earth rotates to the east at an effectively constant angular velocity, but different latitudes have different linear speeds A point at the equator has to go farther in a day than a point in Ohio, so it must go faster(7GG3) Explore the engineeringdesign process going to the Moon!Label parts of water cycle diagrams (7CC1) Select parts of water cycle diagrams (7CC2) The greenhouse effect (7EE1) Analyze models of the EarthSunMoon system (7GG1) What causes the seasons on Earth?




Cosmic Universe Earth S Atmosphere




Carbon Dioxide Definition A Heavy Colorless Gas That
Greenhouse effect, causing global warming The two most abundant gases in the atmosphere, nitrogen (comprising 78% of the dry atmosphere) and oxygen (comprising 21%), exert almost no greenhouse effect Instead, the greenhouse effect comes from molecules that are more complex and much less common Water vapour is the most important greenhouseGreenhouse effect diagram provided by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC, wwwipccch ) is an organization with 195 member countries through which scientists work together to collect and analyze information about climate change from studies all over the worldThe greenhouse effect itself is a perfectly natural phenomenon and, without it, the Earth would be a much colder place But as is often the case, too much of a good thing can have negative consequences, and an unnatural buildup of greenhouse gasses can lead to a
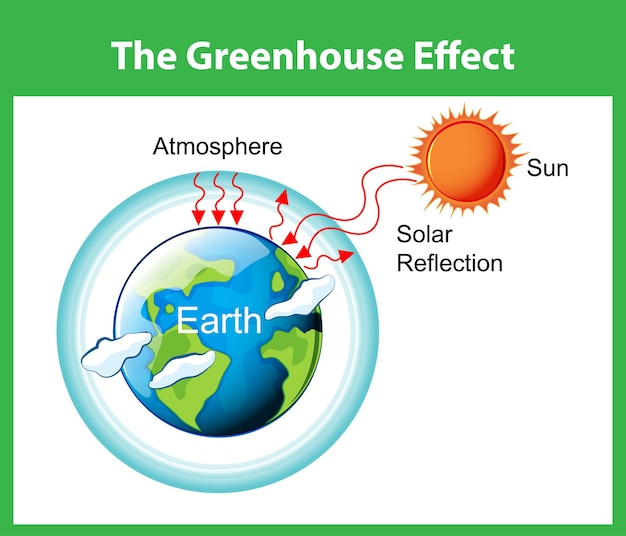



Free Vector The Greenhouse Effect Diagram
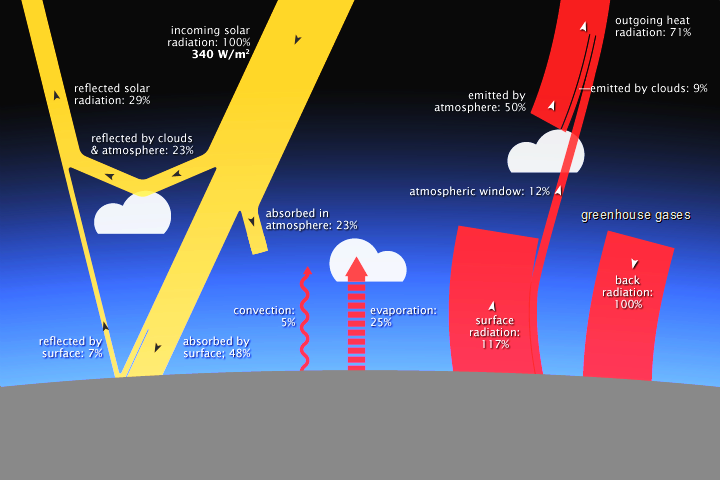



File Diagram Showing The Earth S Energy Budget Which Includes The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Png Wikimedia Commons
I2 Label the above diagram with the approximate surface temperature of the Sun termed the "enhanced greenhouse effect") Your diagram must include labels for the initial change and each forcing/response Explain why it is a positive feedback loop Bonus 2Have students create a diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect using paper, markers, etc Tell them that they will be asked to go home and explain the Greenhouse Effect and global warming to a family member using their diagram as part of a homework assignment Have them practice presenting global warming using their diagrams with peer partnersThe greenhouse effect of Venus From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux over the surface of Venus It is approximately 661 W/m2 Venus is very reflective of solar radiation In fact, it has a reflectivity (or albedo) of 08, so the planet absorbs approximately 661 X 02 = 132 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals the
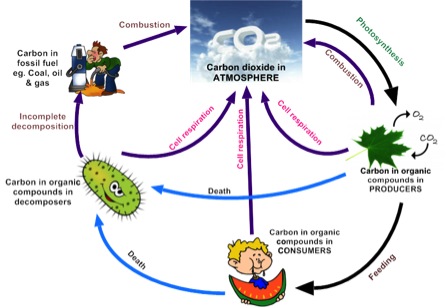



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
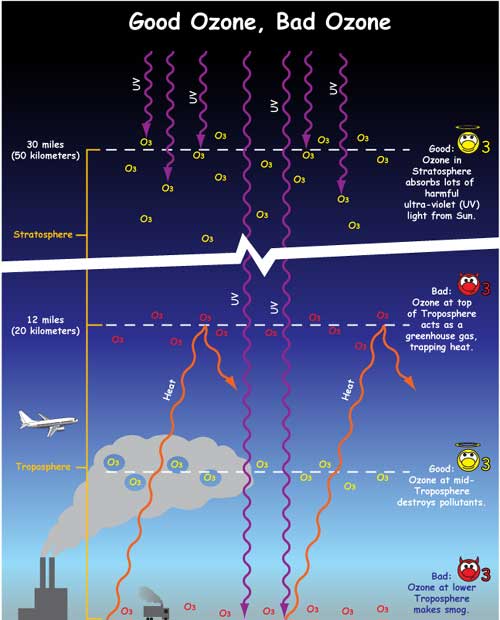
Carbon Cycle and the Greenhouse Effect APES Influential Greenhouse Gases For each of the following, list WHAT they are, WHERE they are found and HOW they affect climate Carbon Dioxide (CO2) A colorless, odorless gas found when organic matter is burned with the presence of oxygen It affects the climate by warming the earth23 List four greenhouse gases (1) Methane (CH 4) (3) Water Vapor (H 2O) (2) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) (4) Nitrous oxide (N 2O) 24 Use the axes to the right for the following a Draw a line representing the Earth's atmosphere and label each layer of the Earth's atmosphere and identify where the greenhouse effect occurs and the ozone layer is 1 The diagram shows a food web from a habitat snake cricket shrew hawk frog marsh grass grasshopper cattail (a) Use information in the food web to complete the table The first one has been done for you (4) number of organisms 8 enhanced greenhouse effect




The Albedo Effect Or Greenhouse Effect Source Sankey Diagram Efectos Del Calentamiento Global Gases Invernadero Cambio Climatico



Draw A Well Labelled Diagram To Explain The Greenhouse Knowledgeboat
Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back toSulfur Hexafluoride (SF6) Potent greenhouse gas, very persistent ( Greenhouse Atmosphere Let's Heat Things Up!




A With The Help Of Well Labeled Diagram Explain Water Cycle In Nature B How Is Green House Effe Youtube



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources
Figure 121 Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Gas 04 Click for a text description of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas 04 Carbon dioxide/CO 2 fossilfuel use 566% Carbon dioxide/CO 2 (other) 28% Carbon dioxide/CO 2 (deforestation, decayEarth's greenhouse effect is basic to understanding global warming Like many natural processes, this effect is best understood in terms of energy flows For starters, Figure 6 shows the energy flow near the surface of an imaginary Earth that has no greenhouse gases (these are trace gases, mainly water vapor and CO 2 ) but has an otherwise The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides




6 Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock




Easy Greenhouse Effect Drawings
(8C4) Plant cell diagrams label parts (8O4) Animal cell diagrams



Variable Weather N Changing Climate Gateway2 Complete Sec 3 Sec 4



Title Climate Change Starter Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Simple



2



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases




Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Worksheet



2



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Illustration Of The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Green House Effect B Draw A Well Labeled Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Brainly In



28 January 17 The Science Of Climate Change Polartrec




Solar Radiation And Global Warming Illustration Stock Image C050 36 Science Photo Library




Snap Diagram Of Greenhouse Effect Image Collections How To Guide And Refrence Photos On Pinterest




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



6 A Simplified Diagram Illustrating The Greenhouse Effect Based On A Download Scientific Diagram



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 165 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Global Carbon Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 165 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Climate Change And The Greenhouse Effect Worksheet Teaching Resources



3



2




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub



The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




5 2 1 Draw And Label A Diagram




Environmental Charts And Diagrams With Private Label Rights 38 Environmental Charts And Diagrams That Commu Environment Greenhouse Effect Environmental Report




Solved Activity 2 Show Your Understanding Of The Greenhouse Chegg Com



2




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




What Is The Greenhouse Effect




Small Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Home Learning Support 2 12 Geography Selsdon Year 5




Small Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Full Size Png Download Seekpng



2



Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Learn Biology




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image



Greenhouse Effect
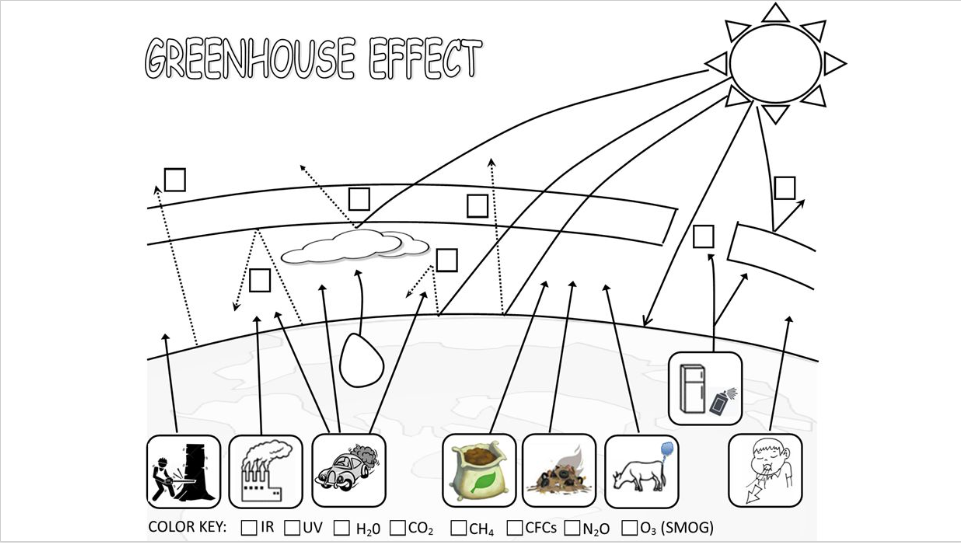



Solved Instructions For Greenhouse Effect Chegg Com
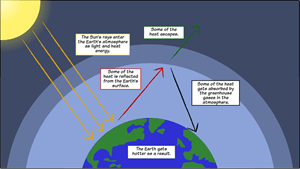



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Carbon Sink Wikipedia



2




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



Clouds Enchanted Learning



2




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education




Rising Sea Levels Vector Illustration Labeled Climate Change Infographics Educational Diagram With Causes And Risks Of Global Warming Water Problem Progress Scheme And Adapting Examples Collection Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube




Geography Global Warming Flashcards Quizlet



The Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect Apes By Reymond P




529 Greenhouse Effect Diagram Illustrations Clip Art Istock




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids




Elly Mtineghe Kabuye Ellymtineghe Profile Pinterest
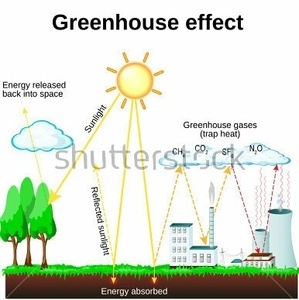



Greenhouse Effect Mind Map




Password Logon Page Greenhouse Gardening Greenhouse Effect Green House Design



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Full Size Png Download Seekpng
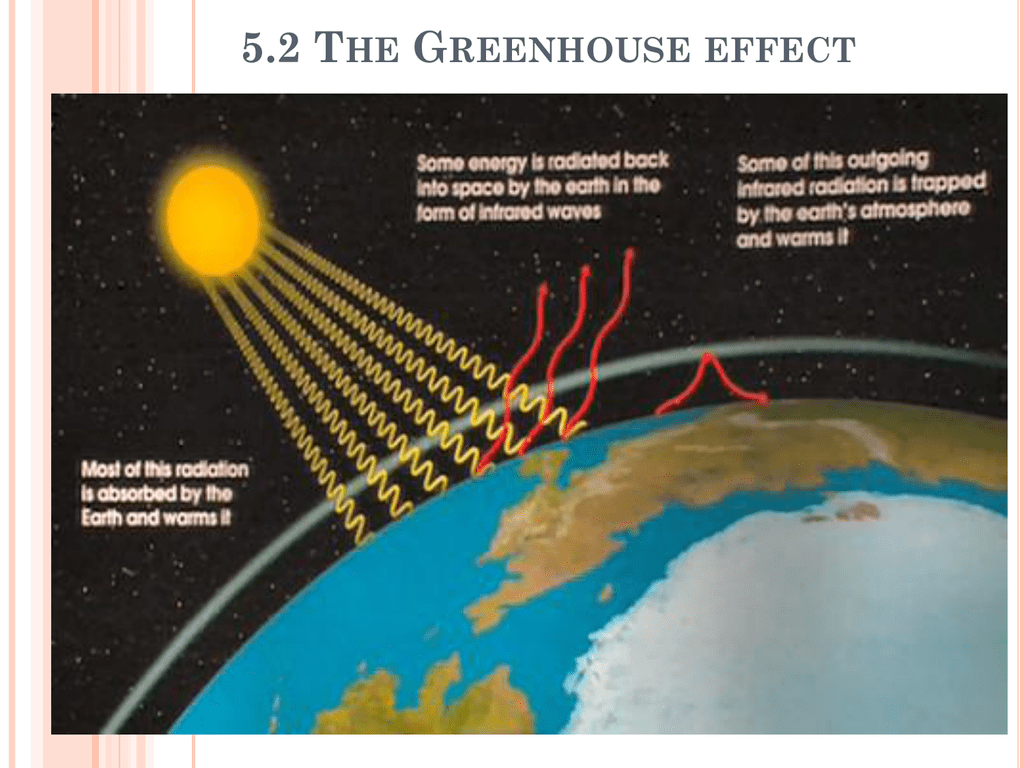



Greenhouse Effect 5 2




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




Draw The Greenhouse Effect Interactive Reading Analysis By Scienceisfun




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Powerpoint




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿